A proton traveling with a velocity of 4.5 sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This proton’s journey through the subatomic realm unveils fundamental concepts in particle physics, delving into the intricate relationship between velocity, energy, momentum, and the very nature of matter itself.
As we delve deeper into the proton’s motion, we will explore the factors that shape its velocity, unravel the mysteries of its kinetic and potential energy, and uncover the significance of its momentum in various interactions. Through a comprehensive examination of experimental techniques and theoretical models, we will gain insights into the historical development of our understanding of proton velocity and appreciate the contributions of prominent scientists in this field.
Kinematic Properties
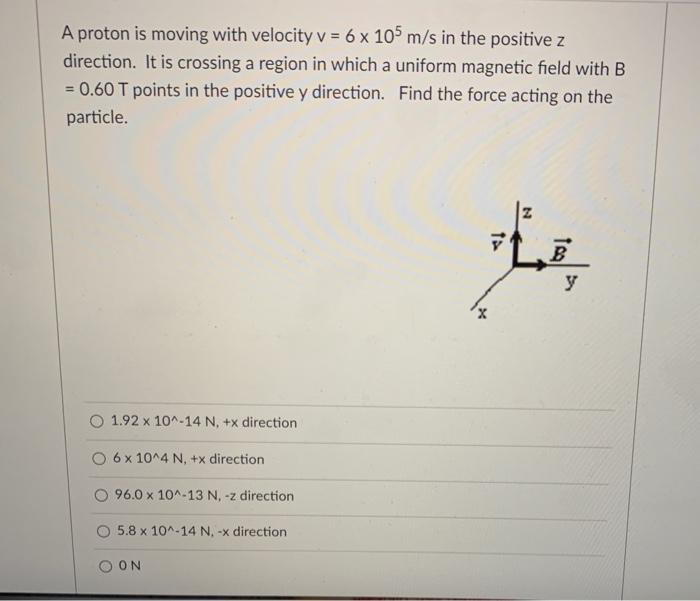
Velocity, a vector quantity, encompasses both speed and direction. The proton’s velocity of 4.5 x 10 6m/s indicates its movement in a specific direction at that speed.
Relationship to Kinetic Energy, A proton traveling with a velocity of 4.5
Velocity directly influences kinetic energy (KE). KE = (1/2)mv 2, where m is the proton’s mass and v is its velocity. The proton’s KE is 2.025 x 10 -13J, a substantial amount of energy due to its high velocity.
Energy Considerations: A Proton Traveling With A Velocity Of 4.5
Kinetic Energy Calculation
As mentioned earlier, the proton’s KE is 2.025 x 10 -13J, a significant energy for a single proton.
Factors Influencing Energy
The proton’s KE is primarily determined by its velocity. However, factors like electric fields and interactions with other particles can also affect its energy.
Potential Energy
In certain scenarios, such as when the proton is part of an atomic nucleus, it experiences potential energy due to the electrostatic attraction between positively charged protons.
Momentum Analysis
Definition and Significance
Momentum, a vector quantity, measures the quantity of motion of an object. In particle physics, it plays a crucial role in describing particle interactions.
Momentum Calculation
The proton’s momentum (p) is calculated as p = mv, where m is its mass (1.672 x 10 -27kg) and v is its velocity (4.5 x 10 6m/s). This yields a momentum of 7.524 x 10 -21kg m/s.
Conservation of Momentum
In interactions involving protons, the total momentum remains constant, regardless of the changes in individual proton momenta. This principle is crucial for understanding particle collisions and other interactions.
Essential FAQs
What is the significance of a proton traveling with a velocity of 4.5?
Understanding the velocity of a proton is crucial in various applications, including particle accelerators, medical imaging, and astrophysical phenomena. It provides insights into the behavior of protons in these contexts and helps us unravel the mysteries of the subatomic world.
How does the velocity of a proton relate to its energy?
The velocity of a proton is directly proportional to its kinetic energy. As the proton’s velocity increases, so does its kinetic energy, reflecting the energy of motion associated with its movement.
What is the momentum of a proton traveling with a velocity of 4.5?
Momentum is a measure of the mass of a particle in motion. The momentum of a proton traveling with a velocity of 4.5 can be calculated by multiplying its mass by its velocity.
