Which statement about glial cells is true? Glial cells, often overshadowed by their neuronal counterparts, play a crucial role in the nervous system’s intricate functioning. This article delves into the fascinating world of glial cells, unraveling their diverse types, functions, and significance in maintaining neural health and mediating neurotransmission.
Beyond their supportive role, glial cells actively participate in regulating synaptic plasticity, influencing neuronal development, and responding to injury or disease. Their dysfunction can have profound implications for nervous system disorders, highlighting their therapeutic potential in neurodegenerative conditions.
Characteristics of Glial Cells: Which Statement About Glial Cells Is True
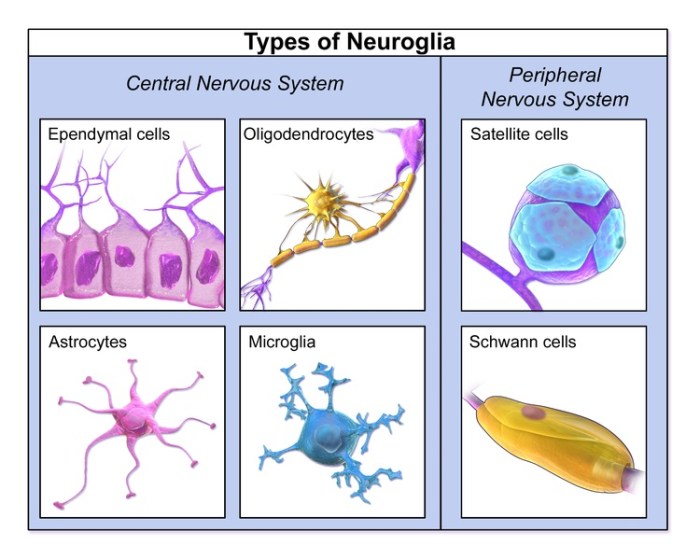
Glial cells, also known as neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells that play vital roles in supporting and maintaining the nervous system. They differ from neurons in their morphology, function, and developmental origin. Unlike neurons, which are responsible for transmitting electrical signals, glial cells provide structural and metabolic support, regulate neuronal activity, and maintain homeostasis within the nervous system.
Glial cells are characterized by their smaller size, lack of axons and dendrites, and the presence of specialized structures such as microfilaments and intermediate filaments. They outnumber neurons by approximately 10:1 and are highly diverse, with different types of glial cells performing specific functions in different regions of the nervous system.
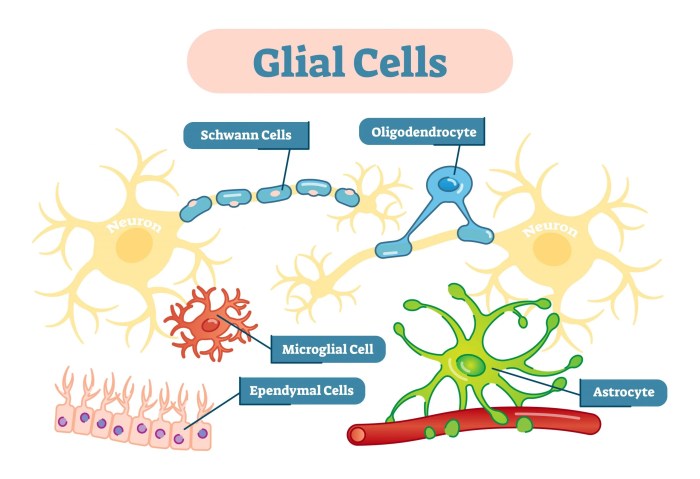
Types of Glial Cells
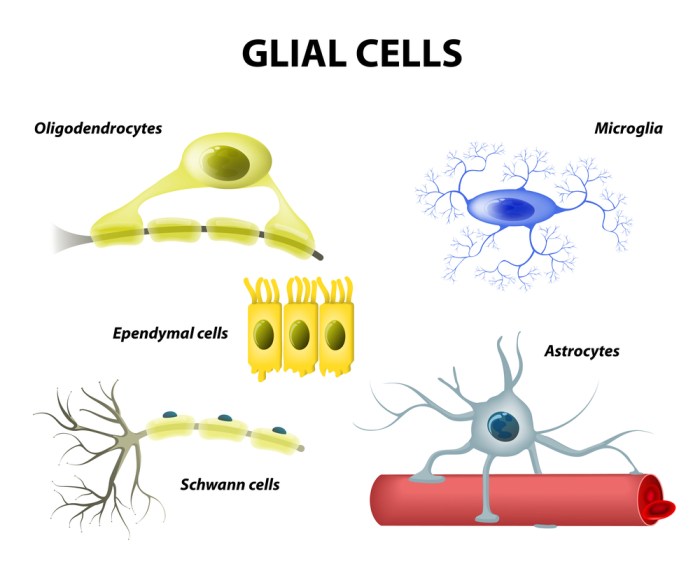
Astrocytes
- Star-shaped cells that provide structural support and regulate the extracellular environment.
- Control ion balance, pH, and neurotransmitter levels.
- Guide neuronal migration and synapse formation during development.
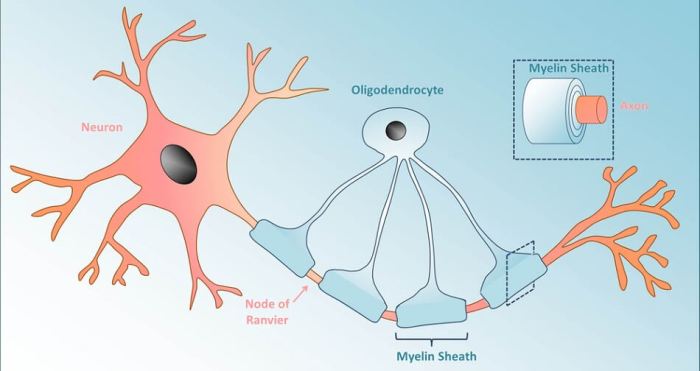
Oligodendrocytes
- Produce myelin sheaths that insulate axons in the central nervous system, increasing the speed of nerve impulses.
- Support and nourish neurons, and contribute to the maintenance of the blood-brain barrier.
Microglia
- Immune cells that monitor the brain for pathogens and damaged neurons.
- Phagocytize debris and release cytokines that can promote inflammation.
- Contribute to synaptic pruning during development and in response to injury.
Schwann Cells, Which statement about glial cells is true
- Similar to oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells produce myelin sheaths in the peripheral nervous system.
- Wrap around axons in a spiral manner, forming a myelin sheath that is thicker than that produced by oligodendrocytes.
Glial Cells and Neurotransmission
Glial cells play a crucial role in regulating neurotransmission and synaptic plasticity.
- Astrocytes control the extracellular concentration of neurotransmitters by releasing glutamate transporters and synthesizing neurotransmitter precursors.
- Oligodendrocytes regulate the speed and efficiency of neurotransmission by insulating axons with myelin sheaths.
- Microglia can release cytokines that modulate synaptic function and plasticity.
Dysfunction of glial cells has been implicated in various neurological disorders, including schizophrenia, depression, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Glial Cells and Nervous System Development
Glial cells are essential for the development and maturation of the nervous system.
- Astrocytes guide neuronal migration and provide structural support during brain development.
- Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells produce myelin sheaths that increase the speed and efficiency of nerve impulses.
- Microglia play a role in synaptic pruning, eliminating excess synapses during development.
Impaired glial function can lead to neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism spectrum disorder and cerebral palsy.
Glial Cells and Nervous System Repair
Glial cells respond to injury or disease in the nervous system by undergoing a process called gliosis.
- Astrocytes and microglia form a glial scar that isolates the damaged area and prevents the spread of damage.
- Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells attempt to remyelinate damaged axons, although this process is often incomplete.
Targeting glial cells in therapeutic strategies could improve outcomes after nervous system injury or disease.
FAQ Compilation
What is the primary function of glial cells?
Glial cells provide structural and functional support to neurons, maintaining the integrity of the nervous system.
How do glial cells contribute to neurotransmission?
Glial cells regulate the release, uptake, and recycling of neurotransmitters, influencing synaptic function and plasticity.
What is the role of glial cells in nervous system development?
Glial cells guide neuronal migration, provide structural support, and promote synapse formation, shaping the architecture of the nervous system.