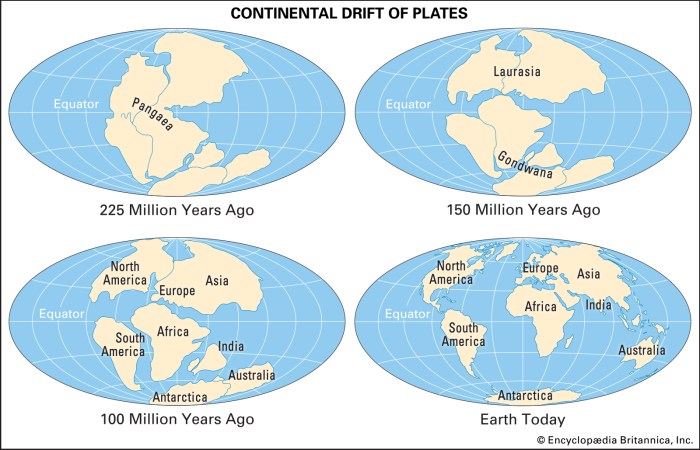
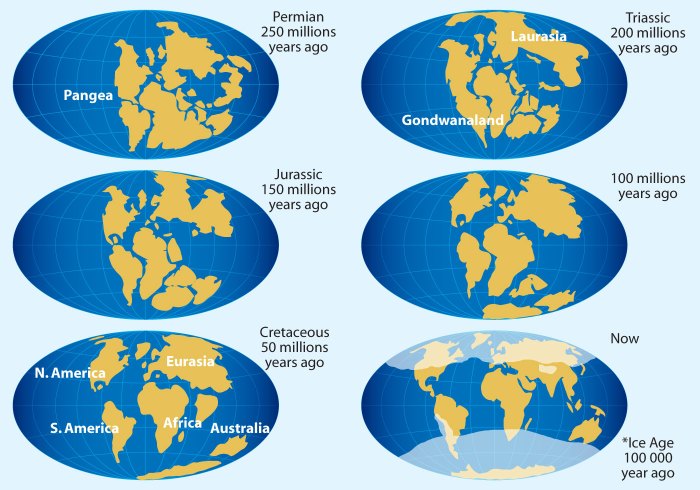
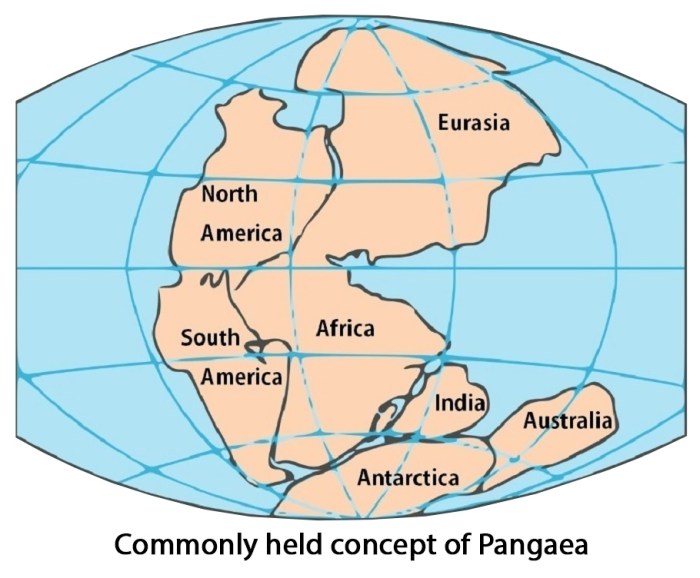
Select the true statement about continental drift – Continental drift, the theory that the Earth’s continents have moved over time, has revolutionized our understanding of the planet’s history and processes. This article examines the evidence supporting continental drift, explores the mechanisms driving it, and discusses its implications for Earth’s geography, climate, and biodiversity.
The concept of continental drift was first proposed in the early 20th century, but it gained widespread acceptance only after the advent of plate tectonics theory in the 1960s. Today, continental drift is a cornerstone of modern Earth science, providing a framework for understanding the dynamic nature of our planet.
History of Continental Drift Theory
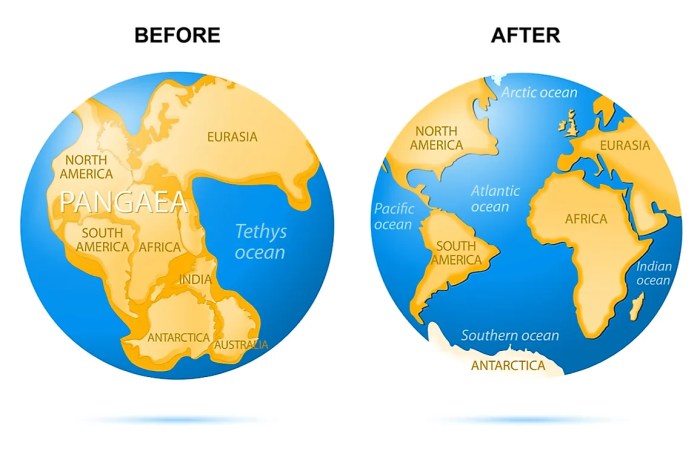
The concept of continental drift, the idea that the continents have moved over time, emerged in the late 19th century. Early observations, such as the matching of rock formations and fossils across continents, led to the hypothesis that the continents were once connected.
Key scientists involved in the formulation of the theory include Alfred Wegener, who proposed the theory in 1912, and Arthur Holmes, who provided supporting evidence from paleomagnetism.
Evidence Supporting Continental Drift
Geological evidence, such as the matching of rock formations and fossils across continents, provides strong support for continental drift. These similarities indicate that the continents were once connected and have since drifted apart.
Paleomagnetic evidence also supports continental drift. The orientation of magnetic minerals in rocks records the Earth’s magnetic field at the time the rocks were formed. By studying the paleomagnetic record, scientists have determined that the continents have moved relative to the Earth’s magnetic poles.
Ocean floor mapping and magnetic anomalies have also provided evidence for continental drift. The discovery of mid-ocean ridges and magnetic stripes on the ocean floor supports the idea of seafloor spreading, which is a key mechanism of continental drift.
Mechanisms of Continental Drift
The proposed mechanisms for continental drift include mantle convection and seafloor spreading. Mantle convection is the movement of the Earth’s mantle, which is the layer beneath the crust. This movement drives the plates that make up the Earth’s crust.
Seafloor spreading is the process by which new oceanic crust is formed at mid-ocean ridges. As new crust is created, the older crust moves away from the ridge, carrying the continents with it.
Plate tectonics is the theory that describes the movement of the Earth’s plates. The plates are large, rigid pieces of the Earth’s crust that move relative to each other. Continental drift is one of the main mechanisms of plate tectonics.
Implications of Continental Drift
Continental drift has had a profound impact on the distribution of plant and animal species. As the continents moved, species became isolated from each other, leading to the evolution of new species and the extinction of others.
Continental drift has also played a major role in shaping the Earth’s geography and climate over time. The movement of the continents has created mountain ranges, ocean basins, and other geological features.
Limitations and Criticisms of Continental Drift Theory, Select the true statement about continental drift
The continental drift theory has faced some limitations and criticisms. One limitation is the lack of a complete understanding of the driving forces behind continental drift.
Criticisms of the theory have included the lack of evidence for the existence of a land bridge between the continents and the difficulty in explaining the mechanisms of continental drift.
However, the theory has been refined and expanded over time, and it is now widely accepted as a fundamental principle of geology.
General Inquiries: Select The True Statement About Continental Drift
What is the evidence for continental drift?
There is a wealth of evidence supporting continental drift, including matching rock formations and fossils across continents, paleomagnetic evidence, and the distribution of ocean floor magnetic anomalies.
What is the mechanism driving continental drift?
Continental drift is driven by plate tectonics, the movement of the Earth’s lithosphere in large, rigid plates. Mantle convection, the movement of hot material within the Earth’s mantle, is the primary force behind plate tectonics.
What are the implications of continental drift?
Continental drift has had a profound impact on the Earth’s surface, shaping the distribution of landmasses, oceans, and mountain ranges. It has also played a crucial role in the evolution of life, influencing the distribution of species and the formation of new ecosystems.