Shadow health prioritization and introduction to leadership – Shadow health prioritization and leadership are intertwined concepts that hold immense significance in the healthcare arena. This discourse delves into the essence of shadow health prioritization, its impact on patient outcomes, and the pivotal role of leadership in driving its successful implementation.
By understanding the intricacies of shadow health prioritization and the principles of effective leadership, healthcare professionals can harness their potential to enhance patient care, optimize resource allocation, and ultimately transform the healthcare landscape.
Shadow Health Prioritization

Shadow health prioritization is a process of identifying and prioritizing patients who are at high risk of developing a serious illness or condition. This process can help healthcare providers to focus their resources on the patients who need them most, and it can lead to improved patient outcomes.
There are a number of different ways to implement shadow health prioritization. One common approach is to use a risk assessment tool to identify patients who are at high risk. These tools typically consider a variety of factors, such as the patient’s age, medical history, and lifestyle.
Once patients have been identified as high risk, they can be prioritized for care. This may involve providing them with more frequent checkups, monitoring their condition more closely, or providing them with additional support services.
Shadow health prioritization can be a valuable tool for healthcare providers. By identifying and prioritizing patients who are at high risk, providers can help to ensure that these patients receive the care they need to stay healthy.
Challenges of Shadow Health Prioritization, Shadow health prioritization and introduction to leadership
There are a number of challenges associated with implementing shadow health prioritization. One challenge is that it can be difficult to identify patients who are at high risk. Another challenge is that it can be expensive to provide additional care to high-risk patients.
Despite these challenges, shadow health prioritization can be a valuable tool for healthcare providers. By carefully considering the benefits and risks, providers can implement programs that can improve patient outcomes.
Introduction to Leadership: Shadow Health Prioritization And Introduction To Leadership
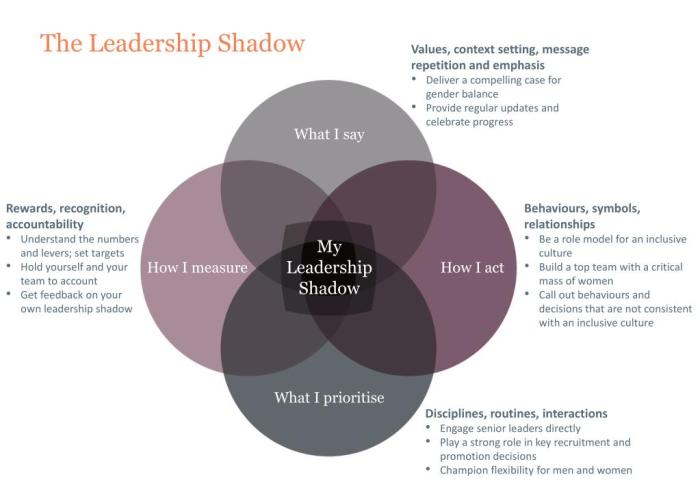
Leadership is the process of influencing others to achieve a common goal. Leaders are people who have the ability to inspire, motivate, and guide others. They are able to create a vision for the future and to motivate others to work towards that vision.
There are many different types of leadership styles. Some leaders are more authoritarian, while others are more democratic. Some leaders are more charismatic, while others are more analytical.
The best leadership style depends on the situation. In some cases, a more authoritarian style may be necessary, while in other cases, a more democratic style may be more effective.
Regardless of the style, all leaders share some common characteristics. They are all able to inspire, motivate, and guide others. They are also able to create a vision for the future and to motivate others to work towards that vision.
Key Principles of Leadership
There are a number of key principles of leadership. These principles include:
- Vision:Leaders have a clear vision for the future and are able to communicate that vision to others.
- Inspiration:Leaders are able to inspire others to believe in their vision and to work towards that vision.
- Motivation:Leaders are able to motivate others to take action and to achieve their goals.
- Guidance:Leaders are able to provide guidance and support to others.
- Trust:Leaders are able to build trust with others and to create a sense of community.
These are just a few of the key principles of leadership. By following these principles, leaders can create a positive and productive work environment and can help their teams to achieve their goals.
Shadow Health Prioritization and Leadership

Shadow health prioritization and leadership are interconnected. Leaders play a critical role in implementing and sustaining shadow health prioritization programs. They are also responsible for creating a culture of patient-centered care, which is essential for the success of any shadow health prioritization program.
Leaders can use shadow health prioritization to improve patient care in a number of ways. For example, they can use shadow health prioritization to:
- Identify patients who are at high risk of developing a serious illness or condition.
- Prioritize care for patients who are at high risk.
- Provide additional support services to patients who are at high risk.
- Monitor the outcomes of patients who are at high risk.
By using shadow health prioritization, leaders can help to ensure that patients receive the care they need to stay healthy.
The Role of Leaders in Shadow Health Prioritization
Leaders play a critical role in the implementation and sustainability of shadow health prioritization programs. They are responsible for:
- Creating a culture of patient-centered care.
- Providing the resources necessary to implement and sustain a shadow health prioritization program.
- Monitoring the outcomes of a shadow health prioritization program.
- Making adjustments to a shadow health prioritization program as needed.
By playing these roles, leaders can help to ensure that shadow health prioritization programs are successful and that patients receive the care they need to stay healthy.
Case Study
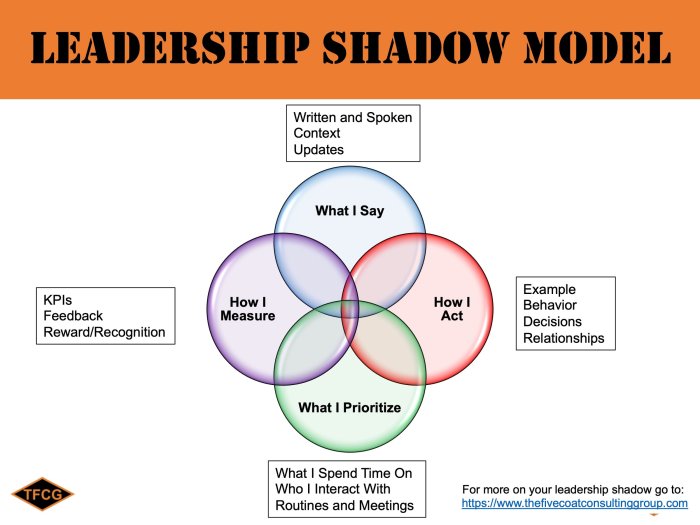
The following is a case study of a healthcare organization that has successfully implemented shadow health prioritization.
The organization is a large, urban hospital. The hospital has a high population of patients who are at high risk of developing a serious illness or condition. In the past, the hospital had difficulty providing these patients with the care they needed.
In 2015, the hospital implemented a shadow health prioritization program. The program uses a risk assessment tool to identify patients who are at high risk. These patients are then prioritized for care. The hospital also provides additional support services to these patients.
The shadow health prioritization program has been a success. The hospital has seen a decrease in the number of patients who are admitted to the hospital. The hospital has also seen a decrease in the length of stay for patients who are admitted to the hospital.
The success of the shadow health prioritization program is due to a number of factors. One factor is the strong leadership of the hospital’s CEO. The CEO is a strong advocate for patient-centered care. He has also provided the resources necessary to implement and sustain the shadow health prioritization program.
Another factor in the success of the shadow health prioritization program is the hospital’s culture of patient-centered care. The hospital’s staff is committed to providing high-quality care to all patients. This commitment is reflected in the way that the staff interacts with patients and in the way that the staff provides care.
The shadow health prioritization program is a valuable tool for the hospital. The program has helped the hospital to improve the care that it provides to patients who are at high risk of developing a serious illness or condition.
Common Queries
What is the primary objective of shadow health prioritization?
Shadow health prioritization aims to identify and prioritize patients who are at high risk of adverse events or poor outcomes, enabling healthcare providers to allocate resources and interventions more effectively.
How does leadership contribute to the success of shadow health prioritization programs?
Effective leadership provides vision, support, and accountability for shadow health prioritization initiatives. Leaders foster a culture of collaboration, innovation, and data-driven decision-making, which are essential for the program’s success.
What are some common challenges associated with implementing shadow health prioritization?
Challenges may include data integration issues, resistance to change, resource constraints, and the need for ongoing monitoring and evaluation to ensure the program’s effectiveness.