Psychologists who advocate the evolutionary view explain behavior through the lens of adaptation, genetics, and environment. This perspective has revolutionized our understanding of human behavior, offering insights into the origins and functions of our thoughts, feelings, and actions.
Evolutionary theory posits that behaviors are shaped by natural selection, which favors traits that enhance survival and reproduction. This perspective has led to a deeper understanding of the adaptive nature of human behavior, from mate selection to altruism.
Evolutionary Perspective in Psychology: Psychologists Who Advocate The Evolutionary View Explain Behavior Through
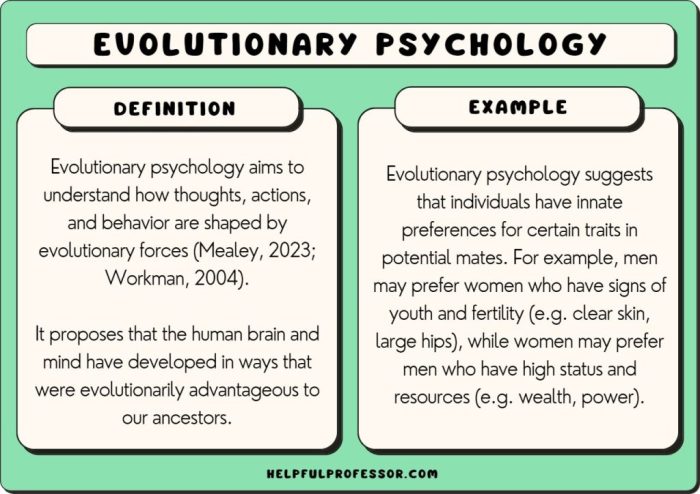
The evolutionary perspective in psychology explains behavior through the lens of evolutionary theory. It posits that behaviors have evolved over time to enhance the survival and reproduction of individuals and their genes.
Evolutionary theory suggests that behaviors that promote survival and reproduction are more likely to be passed on to future generations. Over time, this process leads to the accumulation of adaptive behaviors within a population.
Behavior as Adaptation, Psychologists who advocate the evolutionary view explain behavior through
According to the evolutionary perspective, behaviors are adaptations that have evolved to solve specific problems faced by our ancestors. For example, fear responses evolved to protect us from danger, while social behaviors evolved to facilitate cooperation and resource sharing.
Natural selection favors behaviors that increase an individual’s fitness, which is the ability to survive and reproduce. Behaviors that enhance fitness are more likely to be inherited and passed on to future generations.
Genetic and Environmental Influences
The evolutionary perspective recognizes the interplay between genetic and environmental factors in shaping behavior. Genes provide the raw material for behavioral development, while the environment influences how those genes are expressed.
Evidence supports both genetic and environmental contributions to behavior. For example, twin studies show that identical twins share more behavioral similarities than fraternal twins, suggesting a genetic influence. However, adoption studies indicate that adopted children share more behavioral similarities with their biological parents than their adoptive parents, suggesting an environmental influence.
Evolutionary Explanations for Specific Behaviors
Evolutionary theory has been used to explain a wide range of human behaviors, including:
- Aggression
- Altruism
- Mate selection
- Parental care
- Social cooperation
| Behavior | Evolutionary Explanation | Non-Evolutionary Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Aggression | Adaptive response to threats and competition | Learned behavior due to social and environmental factors |
| Altruism | Kin selection and reciprocal altruism | Social norms and empathy |
| Mate selection | Selection for traits that enhance reproductive success | Cultural preferences and social norms |
Criticisms and Limitations
The evolutionary perspective has been criticized for its reliance on speculation and its inability to fully explain all aspects of behavior. Critics argue that evolutionary explanations often lack empirical support and may be overly simplistic.
Additionally, the evolutionary perspective may not fully account for the complexity and diversity of human behavior. Social and cultural factors, as well as individual experiences, play significant roles in shaping our behavior.
Question Bank
What is the core principle of the evolutionary view in psychology?
The core principle is that behaviors are shaped by natural selection, which favors traits that enhance survival and reproduction.
How does natural selection shape behavior?
Natural selection favors behaviors that increase an individual’s chances of surviving and reproducing, passing on their genes to future generations.
What is the interplay between genetic and environmental factors in shaping behavior?
Both genetic and environmental factors influence behavior. Genes provide the blueprint for our physical and psychological traits, while the environment shapes how those traits are expressed.